3월 29일 수업 내용입니다.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<time.h>
int main()
{
char str[50] = "I like C programing";
printf("string: %s \n", str);
str[8] = '\0'; //9번째 요소에 널 문자 저장
printf("string: %s \n", str);
str[6] = '\0'; //7번째 요소에 널 문자 저장
printf("string: %s \n", str);
str[1] = '\0'; //2번째 요소에 널 문자 저장
printf("string: %s \n", str);
return 0;
}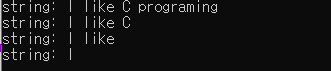
컴파일러가 NULL문자를 만나면 종료로 인식한다.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<time.h>
int main()
{
char str[50];
int idx = 0;
printf("문자열 입력: ");
scanf_s("%s", str, sizeof(str)); //문자열을 입력받아서 배열 str에 저장한다.
printf("입력받은 문자열: %s \n", str);
printf("문자 단위 출력: ");
while (str[idx] != '\0')
{
printf("%c", str[idx]);
idx++;
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<time.h>
int main()
{
char nu = NULL;
char sp = ' ';
printf("%d %d ,", nu, sp);
return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<time.h>
int main()
{
char voca[100];
int len = 0;
printf("영어 단어를 입력 바람: ");
scanf_s("%s", voca, sizeof(voca));
while (voca[len] != NULL)
{
len++;
}
printf("입력한 영어단어 길이는 %d \n", len);
return 0;
}
글자 문자 길이값 알아내기 및 글자 뒤집기
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<time.h>
int main()
{
char voca[100];
int len = 0;
printf("영어 단어를 입력 바람: ");
scanf_s("%s", voca, sizeof(voca));
while (voca[len] != NULL)
{
len++;
}
printf("입력한 영어단어 길이는 %d \n", len);
for (int i = 0; i < len / 2; i++)
{
char temp = voca[i];
voca[i] = voca[(len - i) - 1];
voca[(len - i) - 1] = temp;
}
printf("뒤집힌 영단어: %s \n", voca);
return 0;
}가장큰 비트 값을 가진 아스키코드 찾기
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<time.h>
int main()
{
char voca[100];
int len = 0;
char max = 0;
printf("영어 단어를 입력 바람: ");
scanf_s("%s", voca, sizeof(voca));
while (voca[len] != NULL)
{
len++;
}
printf("입력한 영어단어 길이는 %d \n", len);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if (max < voca[i])
max = voca[i];
}
printf("가장 큰 아스키 코드 값의 문자 : %c \n", max);
return 0;
}포인터 변수의 활용
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<time.h>
int main()
{
int num1 = 100, num2 = 100;
int* pnum; //포인터의 선언
pnum = &num1; //포인터 pnum이 num1을 가리킴
(*pnum) += 30; //num1 += 30;과 동일
pnum = &num2; //포인터 pnum이 num2를 가리킴
(*pnum) -= 30; //num2 -=30; 과 동일
printf("num1: %d, num2: %d \n", num1, num2);
return 0;
}
변수의 주소를 지정한다는 개념이며 가리킬때마다 대상이 바뀐다.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<time.h>
int main()
{
int num1 = 100, num2 = 100;
int* pnum; //포인터의 선언
pnum = &num1; //포인터 pnum이 num1을 가리킴
pnum += 30; //num1 += 30;과 동일
pnum = &num2; //포인터 pnum이 num2를 가리킴
pnum -= 30; //num2 -=30; 과 동일
printf("num1: %d, num2: %d \n", &num1, &num2);
return 0;
}
코드를 살짝 바꿔 본다면 위와 같이 주소값이 출력된다.
*이 포함되면 주소 안에 있는 값에 영향을 준다.
*이 없다면 값에 영향을 줄 수 없다.

문제1번 답
더보기
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<time.h>
int main()
{
int num = 10;
int* ptr1 = #
int* ptr2 = ptr1;
(*ptr1)++;
(*ptr2)++;
printf("%d \n", num);
return 0;
}
첫번째 행, num을 10으로 초기화 했다.
두번째 행, ptr1의 주소에 값으로 변수 num을 저장한다.
세번째 행, ptr2의 주소에 값으로 ptr1의 주소가 저장된다. ptr1의 앞에*을 넣지 않았기 때문.
4번째 행, ptr1의 값이 ++ 된것이므로 11이 될 것이다.
5번째 행, ptr2의 값은 ptr1의 주소로 되어있다. 여기서 ++연산이 되어도 num 값에는 영향이 없을 것이다.
따라서 결과는 num 을 출력하는 것이기 때문에 11이 되지 않을까?
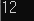
내 예상이 틀렸다 결과값은 12가 나왔다.
ptr2 = ptr1 이 선언된 시점에서
num 변수가 2개의 주소를 가지게 된다.
문제 2번답
더보기
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<time.h>
int main()
{
int num1 = 10, num2 = 20;
int* ptr1 = &num1;
int* ptr2 = &num2;
printf("%d %d \n", *ptr1, *ptr2);
*ptr1 += 10;
*ptr2 -= 10;
printf("%d %d \n", *ptr1, *ptr2);
ptr1 = &num2;
ptr2 = &num1;
printf("%d %d \n", *ptr1, *ptr2);
return 0;
}
출력 결과
10 20
20 10
10 20

문제2번 답
더보기
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<time.h>
int main()
{
char voca[100];
int len = 0;
printf("영어 단어를 입력 해주세요: ");
scanf_s("%s", voca, sizeof(voca));
while (voca[len] != NULL)
{
len++;
}
printf("입력한 영어단어 길이는 %d \n", len);
for (int i = 0; i < len / 2; i++)
{
char temp = voca[i];
voca[i] = voca[(len - i) - 1];
voca[(len - i) - 1] = temp;
}
printf("뒤집힌 영단어: %s \n", voca);
return 0;
}문제3번 답
'게임프로그래밍 개발 수업 > C언어 수업' 카테고리의 다른 글
| C언어 04-03 string.h 헤더 파일 사용하기 (0) | 2023.04.03 |
|---|---|
| C언어 수업 포인터와 배열 (0) | 2023.03.30 |
| C언어 1차원 배열, 문자열의 입력과 출력 (0) | 2023.03.28 |
| C언어 for문의 중첩, 지역변수와 전역변수 (0) | 2023.03.27 |
| C언어 스위치문과 3항연산자 (0) | 2023.03.24 |



